JavaScript Typed Arrays
Typed Arrays
Typed arrays are array-like objects designed for handling of raw binary data.
Unlike standard arrays, typed arrays are array buffers of fixed length.
Typed arrays store elements of fixed types like 8-bit integers or 32-bit numbers.
Typed Array Benefits
Typed arrays provide a way to handle binary data as efficiently as arrays in C.
Typed arrays are raw memory, so JavaScript can pass them directly to any function without converting the data to another representation.
Typed arrays are seriously faster than normal arrays for passing data to functions that can use raw binary data. Typed Arrays are highly suitable for:
WebGL and Canvas:
Fast graphics rendering and image processing.File APIs:
Fast reading and writing of local files.Media APIs:
Fast handling of audio and video data.WebSockets:
Efficient binary data transfer over network.
Differences from Regular Arrays
Fixed Length:
Typed Arrays cannot be dynamically resized using methods like push() or pop().Type Restriction:
Elements must adhere to the specified data type of the typed array.Underlying Buffer:
Typed Arrays are views into an ArrayBuffer, allowing direct manipulation of binary data.
Typed Array Types
| Name | Min | Max | Bytes | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Int8Array | -128 | 127 | 1 | byte |
| Uint8Array | 0 | 255 | 1 | octet |
| Uint8ClampedArray | 0 | 255 | 1 | octet |
| Int16Array | -32768 | 32767 | 2 | short |
| Uint16Array | 0 | 65535 | 2 | unsigned short |
| Int32Array | -2147483648 | 2147483647 | 4 | long |
| Uint32Array | 0 | 4294967295 | 4 | unsigned long |
| BigInt64Array | -263 | 263 - 1 | 8 | bigint |
| BigUint64Array | 0 | 264 - 1 | 8 | unsigned bigint |
| Float16Array | -65504 | 65504 | 2 | unrestricted half |
| Float32Array | -3.4e38 | 3.4e38 | 4 | unrestricted float |
| Float64Array | -1.8e308 | 1.8e308 | 8 | unrestricted double |
8 Bit Integers
| Name | Data Type | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Int8Array | Signed integer (byte) | -128/127 |
| Uint8Array | Unsigned integer (octet) | 0/255 |
| Uint8ClampedArray | Unsigned integer (octet) | 0/255 |
Examples
Create a typed array of 10 signed 8-bit integers (byte format):
const myArr = new Int8Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 unsigned 8-bit integers (octet format):
const myArr = new Uint8Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 usigned 8-bit integers (clamped format):
const myArr = new Uint8ClampedArray(10);
Try it Yourself »
Uint8Array vs Uint8ClampedArray
The difference between an Uint8Array and an Uint8ClampedArray is how values are added.
If you set one element in an Uint8ClampedArray to a value outside the 0-255 range, it will default to 0 or 255.
A typed array will just take the first 8 bits of the value.
Note
Typed arrays are not arrays.
isArray() on a typed array returns false.
Many array methods (like push and pop) are not supported by typed arrays.
16-Bits Integers
| Name | Data Type | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Int16Array | Short integer | -32768/32767 |
| Uint16Array | Unsigned short integer | 0/65535 |
Examples
Create a typed array of 10 signed 16-bit integers (short format):
const myArr = new Int16Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 unsigned 16-bit integers (unsigned short format):
const myArr = new Uint16Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
32-Bit Integers
| Name | Data Type | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Int32Array | Signed long integer | -2147483648 / 2147483647 |
| Uint32Array | Unsigned long integer | 0 / 4294967295 |
Examples
Create a typed array of 10 signed 32-bit integers (long format):
const myArr = new Int32Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 unsigned 32-bit integers (unsigned long format):
const myArr = new Uint32Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
64-Bit Integers
| Name | Data Type | Range |
|---|---|---|
| BigInt64Array | Big signed integer | -263/263-1 |
| BigUint64Array | Big unsigned integer | 0/264 |
Examples
Create a typed array of 10 signed 64-bit integers (bigint format):
const myArr = new Bigint64Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 unsigned 64-bit integers (bigint format):
const myArr = new Biguint64Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Floating Point Numbers
| Name | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Float16Array | Half precision - 3 significant decimal digits | -65504 / 65504 |
| Float32Array | Normal precision - 7 significant decimal digits | -3.4e38 / 3.4e38 |
| Float64Array | Double precision- 15 significant decimal digits | -1.8e308 / 1.8e308 |
As specified by the ECMAScript standard, arithmetic in JavaScript shall be done using double-precision floating-point arithmetic:
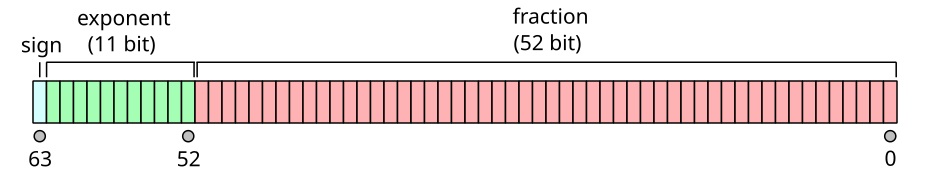
Examples
Create a typed array of 10 floating point numbers in (half precision) 16-bit format:
const myArr = new Float16Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 floating point numbers in (normal precision) 32-bit format:
const myArr = new Float32Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Create a typed array of 10 floating point numbers in (double precision) 64-bit format:
const myArr = new Float64Array(10);
Try it Yourself »
Browser Support
Typed Arrays is an ES6 feature (JavaScript 2015).
ES6 is fully supported in all modern browsers since June 2017:
| Chrome 51 | Edge 15 | Firefox 54 | Safari 10 | Opera 38 |
| May 2016 | Apr 2017 | Jun 2017 | Sep 2016 | Jun 2016 |
Typed Arrays is not supported in Internet Explorer.

